Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants
1. Differentiate between
(a) Respiration and Combustion
(b) Glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle
(c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation
Solution:
a) Respiration and Combustion
Respiration
|
Combustion
|
It is a biochemical process
|
It is a physicochemical process.
|
Temperature stays low
|
Temperature drastically raises
|
Occurs in living cells
|
It is a non-cellular process
|
Energy entrapped in the form of ATP
|
ATP is not required for the combustion process
|
b) Glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle
Glycolysis
|
Krebs Cycle
|
The first step in respiration
|
The second step in respiration
|
Takes place in cytoplasm
|
Takes place in mitochondria
|
Occurs both aerobically and anaerobically
|
Occurs anaerobically
|
Two ATPs are consumed
|
ATPs are not consumed
|
The net gain is 8 ATP’s
|
The net gain is 24 ATP’s
|
It is a linear pathway
|
It is a circular pathway
|
c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation
Aerobic respiration
|
Fermentation
|
Included in the exchange of gases
|
Does not include exchange of gases
|
Oxygen is necessary for aerobic respiration
|
Oxygen should be absent for the fermentation process
|
Respiratory material is completely oxidised
|
Respiratory material is incompletely oxidised
|
The end products are inorganic
|
At least one product is organic
|
2. What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
Solution:
Organic substrates that are oxidised during respiration to liberate energy inside the living cells are respiratory substrates. Carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids are the most common respiratory substrate.
3. Give the schematic representation of glycolysis?
Solution:
Schematic representation of glycolysis is as follows:
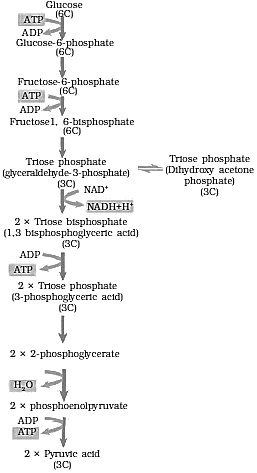
4. What are the main steps in aerobic respiration? Where does it take place?
Solution:
Main steps in aerobic respiration are as follows
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm(cytosol) where glucose is broken down to pyruvic acid.
- Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetyl coenzyme-A: Takes place inside the mitochondrial matrix.
- TCA or Krebs cycle takes place in Mitochondrial matrix where pyruvic acid is oxidized to transform the energy contained in these molecules into ATP.
- Electron transport chain occurs in mitochondrial membrane involves ATP synthase complex.
5. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs’ cycle.
Solution:
The schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs’ cycle is as follows:

6. Explain ETS.
Solution:
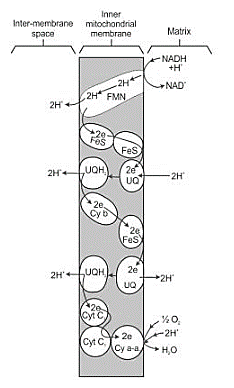
- Electron transport system(ETS) is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane and aids in liberating and using the energy stored in the NADH+H+ and FADH2
- NADH+ H+ , formed while citric acid cycle and glycolysis occurs is oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase or complex I
- Electrons hence produced are conveyed to ubiquinone via FMN
- Similarly, the complex II or FADH2 synthesized during the citric acid cycle is conveyed to ubiquinone
- From ubiquinone electrons are accepted by the complex III or cytochrome bc1 which furthermore gets conveyed to cytochrome c which serves as a mobile carrier between the cytochrome c oxidase complex and complex III comprising of cytochrome a and a3 with copper centers (complex IV) additionally
- When electrons are transferred from each complex, simultaneously other processes occur such as production of the ATP from ADP and the inorganic phosphate through the action of ATP synthase(complex V)
- This amount of ATP production is dependent on the molecule that has been oxidized. 3 ATP molecules are generated by the oxidation of 1 molecule of NADH while 1 FADH2 molecule upon oxidation produces 2 ATP molecules
7. Distinguish between the following:
(a) Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
(b) Glycolysis and Fermentation
(c) Glycolysis and Citric acid Cycle
Solution:
a) Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration
|
Anaerobic respiration
|
Occurs in the presence of the Oxygen
|
Occurs in the absence of Oxygen
|
Involves complete breakdown of respiratory materials.
|
Involves partial breakdown of the gases.
|
Carbon-di-oxide and water are the end products
|
Carbon-dioxide and ethanol are the end products.
|
Involves the exchange of gases
|
Does not include the exchange of gases
|
b) Glycolysis and Fermentation
Glycolysis
|
Fermentation
|
It is the first step in aerobic respiration, and it is common to both aerobic and anaerobic modes of respiration
|
It is anaerobic respiration which does not require Oxygen.
|
It produces pyruvic acid
|
It produces lactic acid and ethanol
|
It produces two molecules of NADH for every glucose molecule.
|
Uses NADH generated during glycolysis
|
It forms two ATP for every glucose molecule
|
It does not produce ATP.
|
c) Glycolysis and Citric acid Cycle
Glycolysis
|
Citric acid cycle
|
Occurs inside cytoplasm
|
Occurs inside mitochondria
|
It is a linear pathway
|
It is a cyclic pathway
|
In Glycolysis glucose is breakdown to pyruvate
|
Acetyl group is broken down completely.
|
The net gain is 8 ATP
|
Net gain is 24 molecules of ATP
|
8. What are the assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
Solution:
Assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP are as follows
- NADH generated inside the mitochondria synthesizes 3 ATP molecules during its oxidation.
- NADH formed during glycolysis sends its reducing power into mitochondria via the shuttle system.
- During oxidation of FADH2, 2 molecules of ATP is produced inside mitochondria
- Formation of 3 ATP in the malate-aspartate shuttle (heart, liver and kidney) and 2 ATP in the glycerol phosphate shuttle (muscles and nerve cells).
9. Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.”
Solution:
Organic substances such as fats, carbohydrates, proteins etc liberate energy when they are disintegrated in the respiratory pathway. This phenomena is said to be catabolic in nature. The respiratory process that serves as a catabolic pathway for the respiratory substrates also serves as an anabolic pathway to produce different metabolic products and secondary metabolites. Thus, the respiratory pathway serves as a catabolic and anabolic pathway. Therefore, the respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.
10. Define RQ. What is its value for fats?
Solution:
The ratio of volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of Oxygen consumed in respiration is called respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio.

RQ is less than 1 when the respiratory substrate is either fat or protein

11. What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Solution:
Oxidative phosphorylation is the conversion of ADP into ATP by electron transport system. Phosphorylation takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane via the ATP synthetase complex when the hydrogen protons pass through it. The energy essential for phosphorylation is derived from the oxidation-reduction phenomena in respiration. Thus the process is known as oxidative phosphorylation.
12. What is the significance of step-wise release of energy in respiration?
Solution:
During respiration single molecule of glucose is disintegrated to generate carbon dioxide and water along with the formation of ATP molecules. If the energy gets released at one go, then most of energy will be lost as heat. In order to synthesize new compounds, the cell should be able to utilize the energy. Hence step-wise release of energy in respiration is most efficient in the conservation of energy.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants is classified under Unit 4 – Plant Physiology. It forms an important part of the unit. This unit contributes to nearly 25% of the total marks which is around 18 marks majorly. This data is collated from past trends to give an idea as to how important the topic is. The information covered in this unit is significant enough to appear in the entrance examinations. It is a valuable resource from which students can grasp maximum information and has been answered precisely and accurately.
The different types of questions that appear in the examination are as follows:
- Knowledge-based
- Application-based
- High-order thinking skills
- Remembering
List of subtopics covered in Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants
Number
|
Subtopic
|
14.1
|
Do Plants Breathe?
|
14.2
|
Glycolysis
|
14.3
|
Fermentation
|
14.4
|
Aerobic Respiration
|
14.5
|
The Respiratory Balance Sheet
|
14.6
|
Amphibolic Pathway
|
14.7
|
Respiratory Quotient
|
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants
Respiration is one of the fundamental processes that is carried out by living entities. All the energy that is required for life processes is obtained by the oxidation of some macromolecules derived from food. Autotrophs can synthesize their food through the process of photosynthesis wherein light energy is trapped and converted into chemical energy. Green plants, different tissues, and cells that are non-green require food for oxidation. Therefore, food can be translocated to all the non-green parts. Since animals are heterotrophic, they derive their nutritional requirements from plants.
The chapter deals with cellular respiration. It is the mechanism of the disintegration of food materials inside the cell to release energy. This energy is trapped to synthesize ATP, which are the energy currencies of a cell.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants
- NCERT solutions are framed in accordance with the textbook data
- Provides answers to all the questions appearing in the same order as provided in the textbook
- It is the ultimate resource for all academic requirements of students following CBSE
- Solutions are provided in the most efficient and effective pattern
- Conceptual knowledge of students can be assessed while referring
- Easily available in a ready-to-download format
Frequently Asked Questions on Respiration in Plants
What are respiratory substrates?
Organic substrates that are oxidised during respiration to liberate energy inside the living cells are respiratory substrates. Carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids are the most common respiratory substrate.
What are the main steps in aerobic respiration?
Main steps in aerobic respiration are as follows
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm(cytosol) where glucose is broken down to pyruvic acid.
- Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetyl coenzyme-A: Takes place inside the mitochondrial matrix.
- TCA or Krebs cycle takes place in Mitochondrial matrix where pyruvic acid is oxidized to transform the energy contained in these molecules into ATP.
- Electron transport chain occurs in mitochondrial membrane involves ATP synthase complex.
Explain ETS?
Electron transport system(ETS) is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane and aids in liberating and using the energy stored in the NADH+H+ and FADH2
What are the assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
Assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP are as follows
- NADH generated inside the mitochondria synthesizes 3 ATP molecules during its oxidation
- NADH formed during glycolysis sends its reducing power into mitochondria via the shuttle system.
- During oxidation of FADH2, 2 molecules of ATP is produced inside mitochondria
- Formation of 3 ATP in the malate-aspartate shuttle (heart, liver and kidney) and 2 ATP in the glycerol phosphate shuttle (muscles and nerve cells).
Define RQ?
The ratio of volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of Oxygen consumed in respiration is called respiratory quotient (RQ) or respiratory ratio.
Comments
Post a Comment